This labs is about creating image from dockerfile.
Youtube Link: Navigation for lab
mkdir doclab cd doclab
Create a dockerfile using vi editor FROM debian:stable LABEL authors="amit" RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y --force-yes apache2 EXPOSE 80
- Save the dockerfile - docker build -t mydeb .
FROM debian:stable: This sets the base image for your Docker image as the official Debian stable image.LABEL authors="amit": This adds a label to your image indicating the author as “amit”. Labels are metadata that can be used to provide information about the image.RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y --force-yes apache2: This command updates the package list and then installs the Apache2 web server package. The-yflag automatically confirms any prompts during the installation process, and--force-yesis used to force installation without confirmation, which can be risky and is generally not recommended.EXPOSE 80: This instruction indicates that the container will listen on port 80. It’s a declaration of the intended network ports that the container will listen on when running.
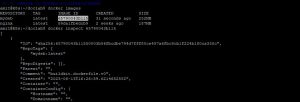
docker images docker inspect <imageid>
COPY and ADD example
Create a docker file dockerfileadd
touch file.txt vi dockerfileadd and copy below code, save it FROM ubuntu:latest # Set a working director inside container WORKDIR /app #Copy file from current directory COPY file.txt /app/ #ADD a directory from the host #ADD /home/lab-user/amit /app/ ADD https://github.com/amitopenwriteup/my_proj/blob/master/k8s-setup.txt /app/ #Till this point copy it in docker file #below command run in the shell docker build -t myweb2 -f dockerfileadd . docker images docker run -it <imageid,from image command> /bin/bash exit
RUN,CMD and ENTRYPOINT
Lab1
1)mkdir test cd test vi date.sh //Copy the below code in date.sh #!/bin/sh echo `date` $@ >> log.txt; cat log.txt; #save date.sh script
chmod 777 date.sh
Create a docker file named mydockerfile and copy the below line
FROM alpine ADD date.sh / RUN ["/date.sh", "image created"]
docker build -t myimage -f mydockerfile .
docker run myimage cat log.txt Check the time
If we run the container several times, we’ll see that the date in our
log file doesn’t change. This makes sense because the run step
executes at image build time, not at the container runtime.
Lab2 Create a new docker file named mydockerfile1
FROM alpine ADD date.sh / RUN ["/date.sh", "image created"] CMD ["/date.sh", "container started"]
docker build -t myimage1 -f mydockerfile1 . docker run myimage1
If we run this multiple times, we’ll see that the image created entry
stays the same. But the container started entry updates with every
run. This shows how cmd indeed executes every time the container
starts.
Lab3: create a new dockerfile mydockerfile2 Lets add two cmd commands.
FROM alpine ADD date.sh / RUN ["/date.sh", "image created"] CMD ["/date.sh", "container started"] CMD ["/date.sh", "container running"]
docker build -t myimage2 -f mydockerfile2 . docker run myimage2
Lab4 : ENTRYPOINT
Create a dockerfile name mydockerfile3
FROM alpine ADD date.sh / RUN ["/date.sh", "image created"] ENTRYPOINT ["/date.sh"]
docker build -t myimage3 -f mydockerfile3 . docker run myimage3 welcome to container